
Smart home and smart building technology has exploded in popularity over the past decade. Homeowners want more control, lower energy bills, better comfort, and systems that make daily life easier. At the same time, developers, architects, and property owners are under pressure to deliver buildings that are efficient, future-proof, and reliable.
With so many smart home technologies on the market, choosing the right one has become increasingly difficult. Many solutions promise simplicity and flexibility but rely on closed ecosystems, cloud services, or short product life cycles. Over time, this can lead to compatibility issues, system failures, or complete obsolescence.
This is where KNX stands apart.
KNX is widely recognised as the leading global standard for smart homes and smart buildings. It is not a brand or a single product, but an open, proven technology used in millions of installations worldwide. For anyone researching KNX system integration tips, understanding why KNX continues to lead the market is essential.
This article explains what KNX is, how it compares to other smart home technologies, and why it is considered the most reliable, scalable, and future-proof solution available today.
What Is KNX?
KNX is an open, international standard for home and building automation. It was developed to allow devices from different manufacturers to communicate with each other seamlessly within a single system.
Unlike many consumer smart home platforms, KNX is not controlled by one company. Instead, it is governed by the KNX Association, which ensures compatibility, certification, and long-term stability across the ecosystem.
A KNX system can control almost every aspect of a building, including: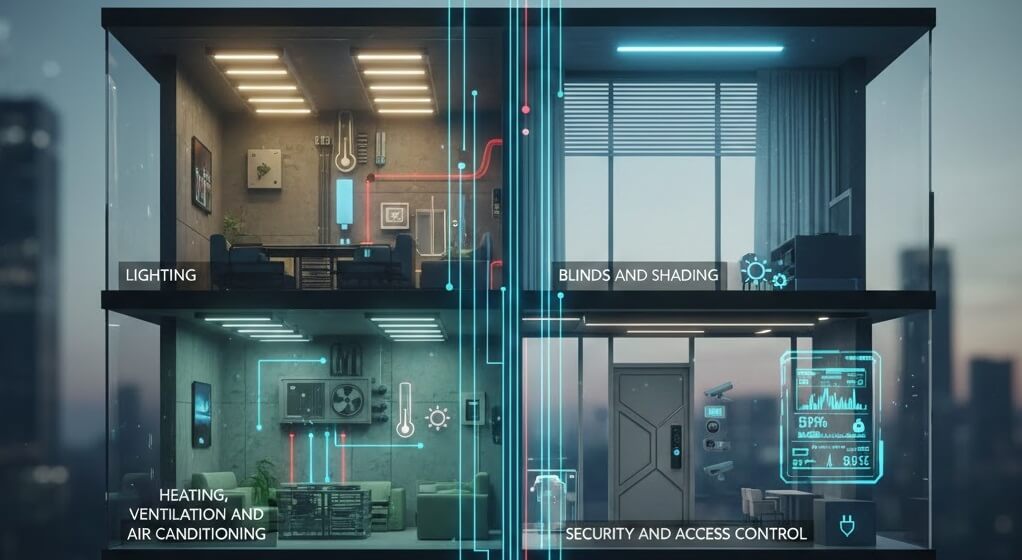
- Lighting
- Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning
- Blinds and shading
- Security and access control
- Energy monitoring
- Automation and scenes
All of these functions operate within one integrated system rather than as isolated devices.
Why Standards Matter in Smart Homes and Smart Buildings
The smart home market is full of innovation, but it is also fragmented. Many popular systems are proprietary, meaning they are locked to one manufacturer’s hardware, software, and cloud services.
This creates several long-term risks:
- Limited compatibility with other products
- Dependence on a single vendor
- Forced upgrades when products are discontinued
- Systems that stop working if cloud services change
Standards like KNX exist to solve these problems.
By defining how devices communicate, KNX ensures that products from hundreds of manufacturers can work together reliably. This protects homeowners and building owners from vendor lock-in and rapid obsolescence.
The 5 W’s of KNX Technology
Who Uses KNX?
KNX is used by a wide range of people and organisations, including:
- Homeowners building high-quality smart homes
- Property developers and landlords
- Architects and designers
- Commercial building owners
- Facilities and energy managers
Although KNX is often associated with premium projects, it is increasingly used in residential homes where reliability and longevity matter.
What Does KNX Control?
KNX is not limited to one function. It can manage:
- Individual lights and whole-house lighting scenes
- Zoned heating and cooling
- Automated blinds and shading
- Security systems and alarms
- Energy usage and monitoring
- Presence and occupancy detection
All of these elements can interact intelligently within a single system.
Where Is KNX Used?
KNX is used worldwide and is especially strong in Europe. It is commonly installed in:
- Private homes and apartments
- Office buildings
- Hotels and hospitality venues
- Schools and universities
- Healthcare and public buildings
Its scalability makes it suitable for both small residential projects and large commercial developments.
Why Do People Choose KNX?
The most common reasons include:
- Exceptional reliability
- Independence from any single manufacturer
- Long-term availability of components
- Flexibility and scalability
- Proven performance over decades
KNX is chosen because it works consistently, not because it is fashionable.
When Is KNX the Right Choice?
KNX is particularly well suited when:
- Long-term reliability is important
- Multiple systems need to work together
- The building may be expanded or adapted
- Vendor lock-in must be avoided
It is especially valuable for new builds and major renovations.
How KNX Differs from Consumer Smart Home Systems
Many consumer smart home platforms are designed for quick installation and low upfront cost. They often rely on Wi-Fi, mobile apps, and cloud servers. While this can work for small setups, it introduces limitations.
KNX takes a very different approach.
Decentralised System Architecture
In a KNX system, intelligence is distributed across devices. There is no single central controller that everything depends on.
Each device can store its own configuration and logic. If one component fails, the rest of the system continues to operate normally.
This eliminates single points of failure and dramatically improves reliability compared to hub-based systems.
Independence from the Cloud
KNX systems operate locally within the building. They do not require an internet connection to function.
This provides several advantages:
- Faster response times
- Improved reliability
- Greater privacy and security
Cloud services can be added if desired, but they are optional rather than essential.
An Open Standard, Not a Brand
KNX is supported by hundreds of manufacturers worldwide. Products from different brands can be mixed freely within the same installation.
This means:
- Greater choice of devices
- Competitive pricing
- Easier upgrades and replacements
- Protection from discontinued products
This openness is one of KNX’s greatest strengths.
KNX vs Other Smart Home Technologies
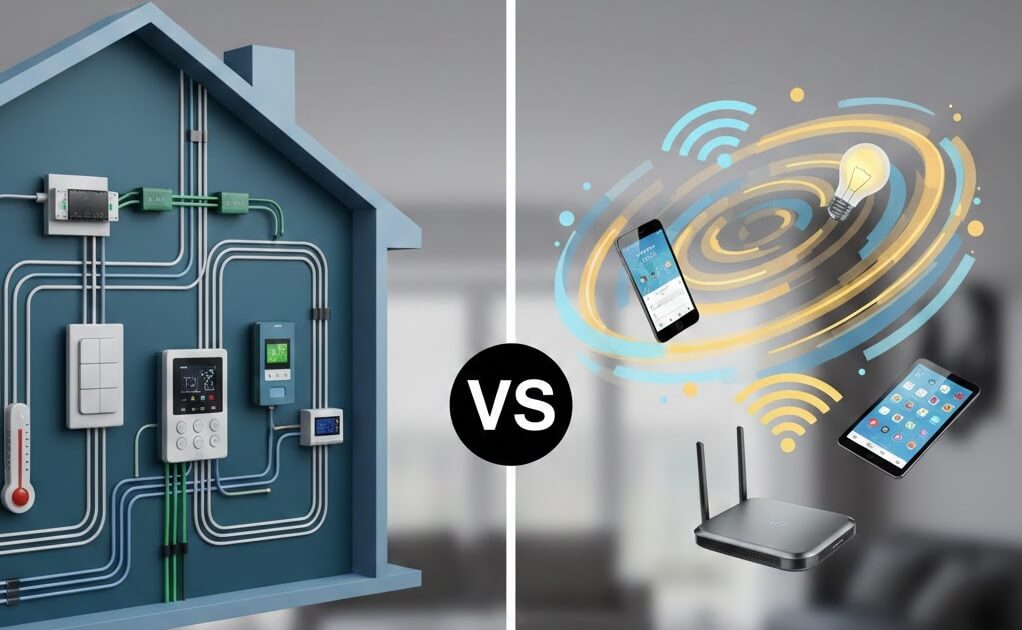

KNX vs Wi-Fi Smart Homes
Wi-Fi smart homes are easy to start with, but they can struggle as systems grow larger. Network congestion, signal interference, and reliability issues become more common as devices are added.
KNX uses dedicated communication designed specifically for automation, making it far more stable and predictable.
KNX vs Proprietary Ecosystems
Proprietary systems often offer polished interfaces but lock users into one vendor. If that vendor changes direction, increases prices, or discontinues products, users have limited options.
KNX avoids this by allowing components to be replaced or upgraded independently.
KNX vs Wireless Protocols
Wireless protocols can be convenient, but they are vulnerable to interference, signal loss, and battery issues.
KNX primarily uses wired communication, which delivers consistent performance regardless of building size or layout. Wireless KNX solutions exist but operate within a robust, standardised framework.
Reliability: The Foundation of KNX
Reliability is the single most important reason KNX is trusted in professional environments.
In smart homes and smart buildings, systems control essential functions such as lighting, heating, and security. These systems must work every time.
KNX achieves this through:
- Decentralised intelligence
- Local control
- Robust communication protocols
- Proven hardware standards
For homeowners, this means a smart home that feels like part of the building, not an add-on.
Scalability and Flexibility
KNX systems are designed to grow and adapt over time.
A system can start with basic lighting and heating control and later expand to include:
- Additional rooms
- New devices
- Advanced automation
- Energy management features
This scalability is a key reason KNX is recommended in many KNX system integration tips guides.
Longevity and Future-Proofing
One of the biggest risks with smart home technology is obsolescence. Many systems become outdated within a few years.
KNX has been in use for decades and continues to evolve while maintaining backward compatibility. Devices installed years ago can still operate within modern systems.
This long lifespan makes KNX a smart investment for anyone thinking beyond short-term trends.
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
KNX plays a major role in energy-efficient building design.
By integrating lighting, heating, shading, and monitoring, KNX systems can:
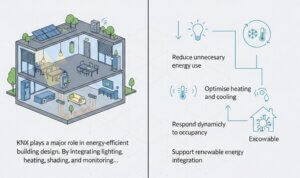
- Reduce unnecessary energy use
- Optimise heating and cooling
- Respond dynamically to occupancy
- Support renewable energy integration
In smart buildings, this contributes directly to sustainability targets and lower operating costs.
User Experience: Powerful Yet Simple
A common misconception is that KNX systems are difficult to use. In reality, the complexity exists during design and installation, not in daily use.
Users can control KNX systems through:
- Wall-mounted switches and keypads
- Touch panels
- Mobile and tablet apps
- Voice assistants
- Fully automated scenes
The result is a clean, intuitive experience for occupants.
Security and Privacy Advantages
Security is an increasing concern in connected homes and buildings.
KNX offers strong security features, including:
- Encrypted communication
- Local system operation
- Controlled access permissions
Because KNX does not rely on third-party cloud platforms, data exposure is significantly reduced.
Common Misconceptions About KNX

“KNX Is Only for Commercial Buildings”
KNX is widely used in commercial environments, but it is equally suitable for residential homes where quality and reliability matter.
“KNX Is Too Expensive”
KNX can have higher upfront costs, particularly for professional design and installation. However, long-term costs are often lower due to reduced maintenance, fewer replacements, and longer system lifespan.
“KNX Is Too Complex”
KNX is complex to design, not to use. With a good integrator, the system is intuitive and easy for homeowners.
KNX System Integration Tips for Successful Projects
Successful KNX installations rely on thoughtful planning and integration.
Key tips include:
- Define clear goals at the start
- Work with a certified KNX integrator
- Plan for future expansion
- Focus on usability, not just features
- Integrate systems rather than isolating functions
Good integration is what transforms KNX from a technical system into a living environment.
The Role of Professional KNX Integrators
KNX is not a DIY system. Professional integrators are essential for:
- System design and architecture
- Device selection
- Programming and commissioning
- Ongoing support and optimisation
Their expertise ensures the system performs reliably and meets the needs of occupants.
KNX in Smart Buildings Beyond the Home
KNX is equally powerful in commercial and public buildings.
In these environments, KNX supports:
- Centralised monitoring and control
- Energy management
- Occupancy-based automation
- Maintenance efficiency
This versatility reinforces KNX’s position as the leading standard.
When KNX May Not Be the Right Choice
KNX may not be suitable for every situation.
It may be unnecessary for:
- Very small, single-room setups
- Temporary installations
- Projects focused solely on minimal upfront cost
Understanding project requirements is key.
Why KNX Continues to Lead the Market
KNX remains the leading standard because it prioritises:
- Stability over trends
- Interoperability over lock-in
- Longevity over novelty
In a fast-moving technology landscape, these qualities matter more than ever.
Final Thoughts: KNX as a Long-Term Investment
Smart homes and smart buildings are long-term investments. The technology chosen today will shape how a space functions for many years.
KNX stands out because it is designed for that reality. It is an open, proven standard built to adapt and endure.
For anyone researching KNX system integration tips or comparing KNX with other smart home technologies, the conclusion is clear. KNX is not just another option. It is the benchmark.
When reliability, flexibility, and future-proofing matter, KNX remains the leading standard for smart homes and smart buildings.